- Introduction: The Evolution of Decorative Metal Mesh
- Understanding Decorative Metal Mesh: Beyond the Basics
- PVD Titanium Coating: The Game-Changing Surface Treatment
- Mesh Patterns and Architectural Applications
- Architectural Applications: Where Decorative Metal Mesh Excels
- 1. Luxury Building Facades
- 2. Premium Interior Design Applications
- 3. Specialized Architectural Uses
- Performance Benefits: The Science Behind the Beauty
- Design Considerations and Customization Options
- Installation Systems and Technical Considerations
- Mounting and Support Systems
- Structural Engineering Considerations
- Weather and Environmental Protection
- Quality Standards and Manufacturing Excellence
- Cost Analysis and Value Engineering
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact
- Future Trends and Innovations
- Conclusion: The Future of Decorative Metal Mesh
Introduction: The Evolution of Decorative Metal Mesh
In the realm of contemporary architecture and luxury interior design, few materials command attention quite like decorative metal mesh. Once relegated to purely functional applications, today's advanced stainless steel mesh systems—enhanced with cutting-edge PVD titanium coatings—have emerged as the material of choice for architects and designers seeking to create spaces that are both visually stunning and exceptionally durable.
From the gleaming facades of luxury hotels to the sophisticated interiors of high-end retail spaces, PVD Ti-coated decorative metal mesh is redefining what's possible in modern design. But what makes this material so extraordinary, and why are leading architects worldwide specifying it for their most prestigious projects?
Understanding Decorative Metal Mesh: Beyond the Basics
What is Decorative Metal Mesh?
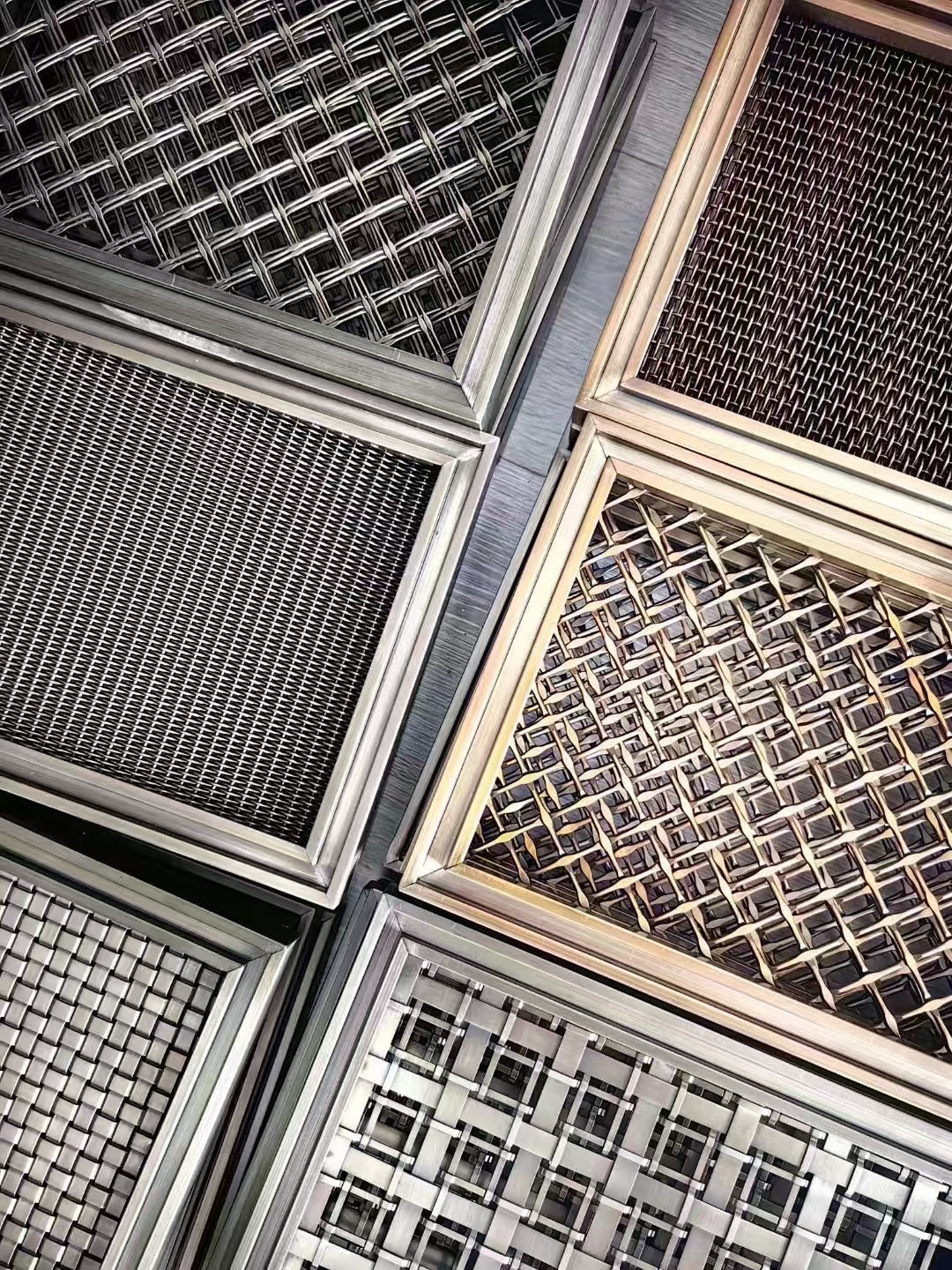
Decorative metal mesh is a flexible, woven or welded material composed of interlaced metal wires or strips that create patterns ranging from simple geometric designs to complex architectural features. Unlike traditional solid panels, mesh offers unique properties of transparency, flexibility, and visual depth while maintaining structural integrity.
The Stainless Steel Foundation
Why Stainless Steel Dominates Premium Applications
Material Excellence:
- Corrosion Resistance: Inherent chromium content provides superior oxidation resistance
- Structural Integrity: High tensile strength supporting large-span installations
- Temperature Stability: Maintains properties across extreme temperature ranges
- Hygiene Benefits: Non-porous surface resists bacterial growth
- Longevity: 50+ year lifespan in most architectural applications
Grade Selection for Decorative Applications
- 304 Stainless Steel: Standard grade for interior and mild exterior applications
- 316/316L Stainless Steel: Marine-grade for coastal and high-corrosion environments
- 321 Stainless Steel: Titanium-stabilized for high-temperature applications
- Duplex Grades: Ultra-high strength for demanding structural applications
PVD Titanium Coating: The Game-Changing Surface Treatment
Understanding PVD Technology
Physical Vapor Deposition Process
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) represents the pinnacle of surface coating technology, creating ultra-thin, ultra-durable layers through a sophisticated vacuum-based process:
- Vacuum Chamber Preparation: Stainless steel mesh placed in high-vacuum environment
- Target Material Vaporization: Titanium target heated to vaporization point
- Ion Bombardment: Energetic ions prepare substrate surface for optimal adhesion
- Atomic Deposition: Titanium atoms deposit uniformly across mesh surface
- Reactive Gas Introduction: Nitrogen or oxygen creates desired compound coatings
Why Titanium Coating Excels
- Hardness: 2000-3000 HV (Vickers Hardness) - harder than tool steel
- Adhesion: Molecular-level bonding with substrate
- Thickness Control: Precise coating thickness from 0.5 to 5 microns
- Uniformity: Even coverage on complex mesh geometries
- Environmental Stability: Inert coating resists chemical attack
PVD Coating Color Options and Finishes
Titanium Nitride (TiN) - Gold Tones
- Color Range: Bright gold to deep brass tones
- Applications: Luxury retail, hotel lobbies, premium residential
- Durability: Excellent wear resistance, fade-proof
- Aesthetic Appeal: Classic luxury appearance with modern performance
Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) - Blue-Black Spectrum
- Color Range: Steel blue to deep black
- Applications: Contemporary architecture, high-tech interiors
- Performance: Superior hardness and corrosion resistance
- Visual Impact: Modern, sophisticated appearance
Chromium Nitride (CrN) - Silver-White Finishes
- Color Range: Bright silver to warm white
- Applications: Clean-room environments, medical facilities
- Benefits: Excellent corrosion resistance, hygienic properties
- Aesthetics: Clean, professional appearance
Multi-Layer Coatings - Rainbow and Gradient Effects
- Technology: Multiple PVD layers creating interference colors
- Color Range: Full spectrum including rose gold, bronze, purple
- Applications: Artistic installations, luxury hospitality
- Uniqueness: Each viewing angle reveals different color nuances
Mesh Patterns and Architectural Applications
Woven Mesh Patterns
Plain Weave
- Construction: Over-under pattern, most common weave
- Characteristics: Uniform appearance, excellent stability
- Applications: General architectural screening, facade elements
- Open Area: 30-70% depending on wire diameter and spacing
Twill Weave
- Construction: Diagonal pattern creating visual texture
- Characteristics: Higher strength, distinctive appearance
- Applications: Decorative panels, artistic installations
- Visual Effect: Dynamic shadow patterns with changing light
Dutch Weave
- Construction: Different wire diameters in warp and weft
- Characteristics: Fine filtration capability, smooth surface
- Applications: Precision screening, high-end interiors
- Performance: Superior strength-to-weight ratio
Welded Mesh Systems
Square Mesh
- Construction: Perpendicular wires welded at intersections
- Characteristics: Rigid structure, precise openings
- Applications: Security screens, architectural panels
- Customization: Wire diameter and spacing fully customizable
Rectangular Mesh
- Construction: Non-square openings for specific applications
- Characteristics: Directional properties, unique aesthetics
- Applications: Facade systems, decorative room dividers
- Design Flexibility: Aspect ratios optimized for specific requirements
Specialty Architectural Meshes
Cable Mesh Systems
- Construction: Stainless steel cables woven or connected
- Characteristics: Large-span capability, dramatic appearance
- Applications: Atriums, curtain walls, artistic installations
- Performance: Excellent for seismic and wind load applications
Expanded Metal Mesh
- Construction: Single sheet expanded to create diamond patterns
- Characteristics: No welded joints, integral construction
- Applications: Walkways, security screens, ventilation panels
- Advantages: Superior strength, no joint failure points
Architectural Applications: Where Decorative Metal Mesh Excels
1. Luxury Building Facades
Hotel and Resort Exteriors
PVD Ti-coated stainless steel mesh creates stunning facade systems that:
- Solar Control: Reduce heat gain while maintaining views
- Privacy Management: Control sight lines without blocking natural light
- Weather Protection: Shield interiors from wind and rain
- Aesthetic Drama: Create dynamic shadow patterns throughout the day
- Brand Identity: Distinctive appearance setting properties apart
Case Example: Luxury resort facades using bronze PVD-coated mesh achieve 40% solar heat reduction while creating Instagram-worthy architectural photography opportunities.
Commercial Office Buildings
- Energy Efficiency: Passive solar control reducing HVAC costs
- Tenant Appeal: Premium appearance attracting high-value tenants
- Maintenance Benefits: Self-cleaning properties reducing upkeep costs
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting increasingly strict energy codes
2. Premium Interior Design Applications
Hotel and Hospitality Interiors
- Lobby Features: Grand-scale decorative elements creating memorable first impressions
- Restaurant Partitions: Intimate dining spaces without complete enclosure
- Bar and Lounge Screens: Sophisticated separation with visual connectivity
- Ceiling Systems: Dramatic overhead elements with integrated lighting
- Elevator Cabs: Luxury finishes elevating the guest experience
Retail and Commercial Interiors
- Store Fixtures: High-end display systems that enhance product presentation
- Security Screens: Elegant protection that doesn't compromise aesthetics
- Space Division: Flexible partitioning systems for adaptable layouts
- Brand Expression: Custom patterns reinforcing corporate identity
- Lighting Integration: Mesh systems optimized for LED backlighting
Residential Luxury Applications
- Room Dividers: Sophisticated space separation in open-plan homes
- Stair Railings: Modern alternatives to traditional balustrade systems
- Wine Cellars: Climate-controlled storage with elegant screening
- Home Theaters: Acoustic treatments that enhance rather than hide
- Outdoor Living: Weather-resistant privacy screens for terraces and patios
3. Specialized Architectural Uses
Cultural and Institutional Buildings
- Museums: Display cases and security screens that don't interfere with exhibits
- Libraries: Quiet study areas with visual connection to main spaces
- Educational Facilities: Durable, low-maintenance solutions for high-traffic areas
- Healthcare: Hygienic surfaces meeting strict cleanliness requirements
Transportation Infrastructure
- Airport Terminals: Large-span decorative elements creating sense of place
- Train Stations: Durable, attractive solutions for high-traffic environments
- Parking Structures: Ventilation screens that enhance rather than detract
- Bridge Architecture: Weather-resistant decorative elements
Performance Benefits: The Science Behind the Beauty
1. Durability and Longevity
Corrosion Resistance
The combination of stainless steel substrate and PVD titanium coating creates unparalleled corrosion resistance:
- Substrate Protection: Stainless steel provides inherent corrosion resistance
- Coating Barrier: PVD layer adds additional protection against environmental attack
- Galvanic Compatibility: Titanium coating prevents galvanic corrosion
- Salt Spray Performance: 2000+ hours ASTM B117 salt spray resistance
- Chemical Resistance: Inert surface resists acids, alkalis, and solvents
Mechanical Durability
- Abrasion Resistance: PVD coatings resist wear from cleaning and handling
- Impact Resistance: Flexible mesh construction absorbs impact energy
- Fatigue Resistance: Woven construction distributes stress effectively
- Temperature Cycling: Maintains properties through freeze-thaw cycles
2. Environmental Performance
UV Stability
- Color Fastness: PVD coatings maintain color indefinitely under UV exposure
- No Chalking: Inorganic coatings don't degrade like organic finishes
- Thermal Stability: Maintains properties at temperatures up to 500°C
- Weathering Resistance: No degradation from rain, snow, or humidity
Energy Efficiency Contributions
- Solar Heat Gain Control: Mesh density optimized for climate conditions
- Natural Ventilation: Promotes air circulation reducing mechanical cooling needs
- Daylighting Optimization: Controls glare while maximizing useful daylight
- Thermal Mass Reduction: Lightweight construction reduces building thermal load
3. Maintenance Advantages
Self-Cleaning Properties
- Smooth Surface: PVD coating creates ultra-smooth surface resisting dirt accumulation
- Hydrophobic Options: Special coatings causing water to sheet off
- Non-Porous Surface: Prevents bacterial growth and staining
- Chemical Resistance: Allows use of strong cleaning agents when necessary
Long-Term Cost Benefits
- No Recoating: PVD coatings last the life of the installation
- Minimal Maintenance: Occasional washing maintains like-new appearance
- No Replacement: 50+ year lifespan eliminates replacement costs
- Insurance Benefits: Fire-resistant, non-combustible material
Design Considerations and Customization Options
Mesh Specification Parameters
Wire Diameter Selection
- Fine Wire (0.5-1.5mm): Elegant appearance, suitable for interior applications
- Medium Wire (1.5-3.0mm): Balance of appearance and strength for most applications
- Heavy Wire (3.0-6.0mm): Maximum strength for structural or security applications
- Mixed Diameters: Different warp and weft wires for specific performance characteristics
Opening Size Optimization
- Fine Mesh (1-5mm openings): Maximum privacy, minimal transparency
- Medium Mesh (5-20mm openings): Balance of privacy and openness
- Coarse Mesh (20-50mm openings): Maximum transparency, minimal visual obstruction
- Variable Mesh: Graduated opening sizes for artistic effects
Color and Finish Customization
Standard PVD Colors
- Gold Spectrum: Light champagne to deep bronze
- Silver Spectrum: Bright chrome to warm pewter
- Black Spectrum: Gunmetal to deep black
- Blue Spectrum: Steel blue to navy
- Special Colors: Rose gold, copper, purple, green (custom formulations)
Surface Texture Options
- Mirror Finish: Maximum reflectivity and light play
- Brushed Finish: Subtle texture reducing fingerprints
- Matte Finish: Non-reflective surface for specific lighting conditions
- Textured Finish: Decorative surface treatments for unique effects
Pattern and Weave Customization
Architectural Weave Patterns
- Geometric Patterns: Regular repeating designs for contemporary aesthetics
- Organic Patterns: Flowing, natural-inspired designs
- Cultural Motifs: Patterns reflecting local architectural traditions
- Corporate Branding: Custom weaves incorporating logos or brand elements
Gradient and Transition Effects
- Density Gradients: Varying mesh density across panel area
- Color Transitions: Multiple PVD colors creating gradient effects
- Pattern Morphing: Gradual pattern changes across large installations
- Lighting Integration: Mesh patterns optimized for backlighting effects
Installation Systems and Technical Considerations
Mounting and Support Systems
Curtain Wall Integration
- Structural Glazing: Seamless integration with glass curtain wall systems
- Pressure Plate Systems: Mechanical attachment allowing easy maintenance access
- Cassette Systems: Pre-fabricated units for rapid installation
- Tensioned Systems: Cable-supported mesh for large-span applications
Interior Installation Methods
- Frame Systems: Rigid frames for permanent installations
- Track Systems: Movable panels for flexible space division
- Suspended Systems: Ceiling-mounted installations
- Freestanding Systems: Self-supporting decorative elements
Structural Engineering Considerations
Load Calculations
- Wind Load: Mesh porosity reduces wind loads compared to solid panels
- Seismic Performance: Flexible mesh construction accommodates building movement
- Dead Load: Lightweight material minimizes structural requirements
- Live Load: Consideration for maintenance access and cleaning loads
Thermal Movement
- Expansion Joints: Accommodating thermal expansion and contraction
- Flexible Connections: Allowing movement without stress concentration
- Material Compatibility: Ensuring compatible thermal expansion rates
- Fastener Selection: Materials and coatings compatible with stainless steel
Weather and Environmental Protection
Water Management
- Drainage Design: Ensuring proper water runoff and drainage
- Ventilation Gaps: Preventing moisture accumulation behind mesh
- Vapor Barriers: Coordinating with building envelope systems
- Ice Load Considerations: Designing for ice accumulation in cold climates
Environmental Durability
- Pollution Resistance: PVD coatings resist urban air pollution
- Salt Air Performance: Marine-grade stainless steel for coastal applications
- Industrial Environments: Chemical-resistant specifications for harsh conditions
- High-Traffic Areas: Abrasion-resistant specifications for public spaces
Quality Standards and Manufacturing Excellence
Material Standards and Certifications
Stainless Steel Standards
- ASTM A240: Standard specification for chromium and chromium-nickel stainless steel plate, sheet, and strip
- ASTM A580: Standard specification for stainless steel wire
- EN 10088: European standard for stainless steel specifications
- JIS G4305: Japanese Industrial Standard for stainless steel plate, sheet and strip
PVD Coating Standards
- ISO 4516: Metallic and other inorganic coatings - Vickers and Knoop microhardness tests
- ASTM B117: Standard practice for operating salt spray apparatus
- ISO 9227: Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres - Salt spray tests
- ASTM D4060: Standard test method for abrasion resistance
Manufacturing Quality Control
Precision Manufacturing Processes
- Wire Drawing: Controlled diameter tolerances ±0.02mm
- Weaving Precision: Automated looms ensuring consistent mesh geometry
- Welding Quality: Robotic welding for consistent joint strength
- PVD Process Control: Real-time monitoring of coating parameters
Quality Assurance Testing
- Dimensional Inspection: Coordinate measuring machines for precise verification
- Coating Thickness: X-ray fluorescence measurement ensuring uniform coating
- Adhesion Testing: Scratch testing and thermal cycling verification
- Corrosion Testing: Accelerated testing simulating decades of exposure
Cost Analysis and Value Engineering
Initial Investment Considerations
Material Cost Factors
- Stainless Steel Grade: Higher grades increase cost but extend lifespan
- Wire Diameter: Heavier wires increase material costs
- Mesh Complexity: Custom weave patterns require specialized manufacturing
- PVD Coating: Premium surface treatment adds 30-50% to material cost
- Panel Size: Larger panels reduce installation costs per square meter
Installation Cost Variables
- System Complexity: Simple mounting systems reduce labor costs
- Access Requirements: Difficult installation locations increase costs
- Structural Requirements: Minimal structural support reduces overall costs
- Coordination Complexity: Integration with other building systems
Long-Term Value Proposition
Lifecycle Cost Analysis
- Maintenance Savings: Minimal maintenance over 50+ year lifespan
- Energy Savings: Reduced HVAC costs through passive environmental control
- Replacement Avoidance: No refinishing or replacement costs
- Property Value Enhancement: Premium materials increase building value
Return on Investment
- Energy Cost Reduction: 15-30% HVAC cost savings in optimized applications
- Maintenance Cost Avoidance: 80% reduction compared to painted steel alternatives
- Insurance Benefits: Fire-resistant, non-combustible material may reduce premiums
- Tenant Attraction: Premium appearance commands higher rents
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Environmental Benefits
Material Sustainability
- Recyclability: 100% recyclable stainless steel content
- Longevity: 50+ year lifespan reduces replacement frequency
- Low Maintenance: Minimal cleaning chemicals required
- Energy Efficiency: Passive environmental control reduces building energy use
Manufacturing Environmental Impact
- PVD Process: No hazardous chemicals or waste products
- Energy Efficiency: Modern manufacturing processes minimize energy consumption
- Waste Reduction: Precision manufacturing minimizes material waste
- Transportation: Lightweight material reduces shipping environmental impact
Green Building Contributions
LEED Credit Contributions
- Materials and Resources: Recycled content and regional materials credits
- Energy and Atmosphere: Building energy performance improvements
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Natural lighting and ventilation enhancement
- Innovation in Design: Advanced materials and systems recognition
BREEAM and Other Standards
- Material Efficiency: Durable materials reducing replacement needs
- Energy Performance: Passive environmental control systems
- Health and Wellbeing: Non-toxic materials and improved indoor environments
- Innovation: Advanced material applications
Future Trends and Innovations
Technological Advances
Smart Mesh Integration
- Sensor Integration: Environmental monitoring embedded in mesh systems
- Electrochromic Coatings: Color-changing coatings responding to environmental conditions
- Photovoltaic Integration: Solar cells integrated with decorative mesh
- LED Integration: Programmable lighting systems within mesh structure
Advanced PVD Technologies
- Nanostructured Coatings: Enhanced properties through nanoscale engineering
- Self-Healing Coatings: Coatings that repair minor damage automatically
- Anti-Microbial Coatings: Permanent antimicrobial properties for healthcare applications
- Photocatalytic Coatings: Self-cleaning and air-purifying surface treatments
Design Evolution
Parametric Design Integration
- Computational Design: AI-assisted mesh pattern optimization
- Performance-Based Design: Patterns optimized for specific environmental conditions
- Mass Customization: Cost-effective custom patterns through advanced manufacturing
- Digital Twin Technology: Virtual modeling for performance prediction
Sustainable Innovation
- Bio-Based Coatings: Environmentally friendly coating alternatives
- Circular Economy: Closed-loop recycling systems for end-of-life materials
- Carbon Neutrality: Manufacturing processes achieving carbon neutral status
- Life Cycle Assessment: Comprehensive environmental impact evaluation
Conclusion: The Future of Decorative Metal Mesh
PVD Ti-coated stainless steel decorative mesh represents the convergence of advanced materials science, sophisticated manufacturing technology, and inspired architectural design. As we've explored throughout this comprehensive guide, this remarkable material offers architects, designers, and building owners an unprecedented combination of beauty, durability, and performance.
Key Advantages Recap
- Unmatched Durability: 50+ year lifespan with minimal maintenance
- Design Flexibility: Unlimited customization options for unique architectural expression
- Environmental Performance: Superior energy efficiency and sustainability credentials
- Cost Effectiveness: Excellent long-term value through reduced maintenance and energy costs
- Aesthetic Excellence: Premium appearance that enhances property value and user experience
Looking to the Future
As building codes become more stringent, environmental concerns intensify, and architectural ambitions grow more sophisticated, PVD Ti-coated decorative metal mesh will continue to evolve and expand its role in the built environment. Smart integration, advanced coatings, and computational design will unlock new possibilities we can only begin to imagine today.
For architects, designers, and developers seeking to create buildings that make lasting impressions while delivering exceptional long-term performance, PVD Ti-coated stainless steel decorative mesh offers a proven path to architectural excellence.
The future of decorative metal mesh is bright—literally and figuratively. With its perfect balance of form and function, beauty and durability, tradition and innovation, this remarkable material will continue to shape the spaces where we live, work, and gather for generations to come.

Share:
Metal Facades: What They Are & Why Use Perforated Sheets