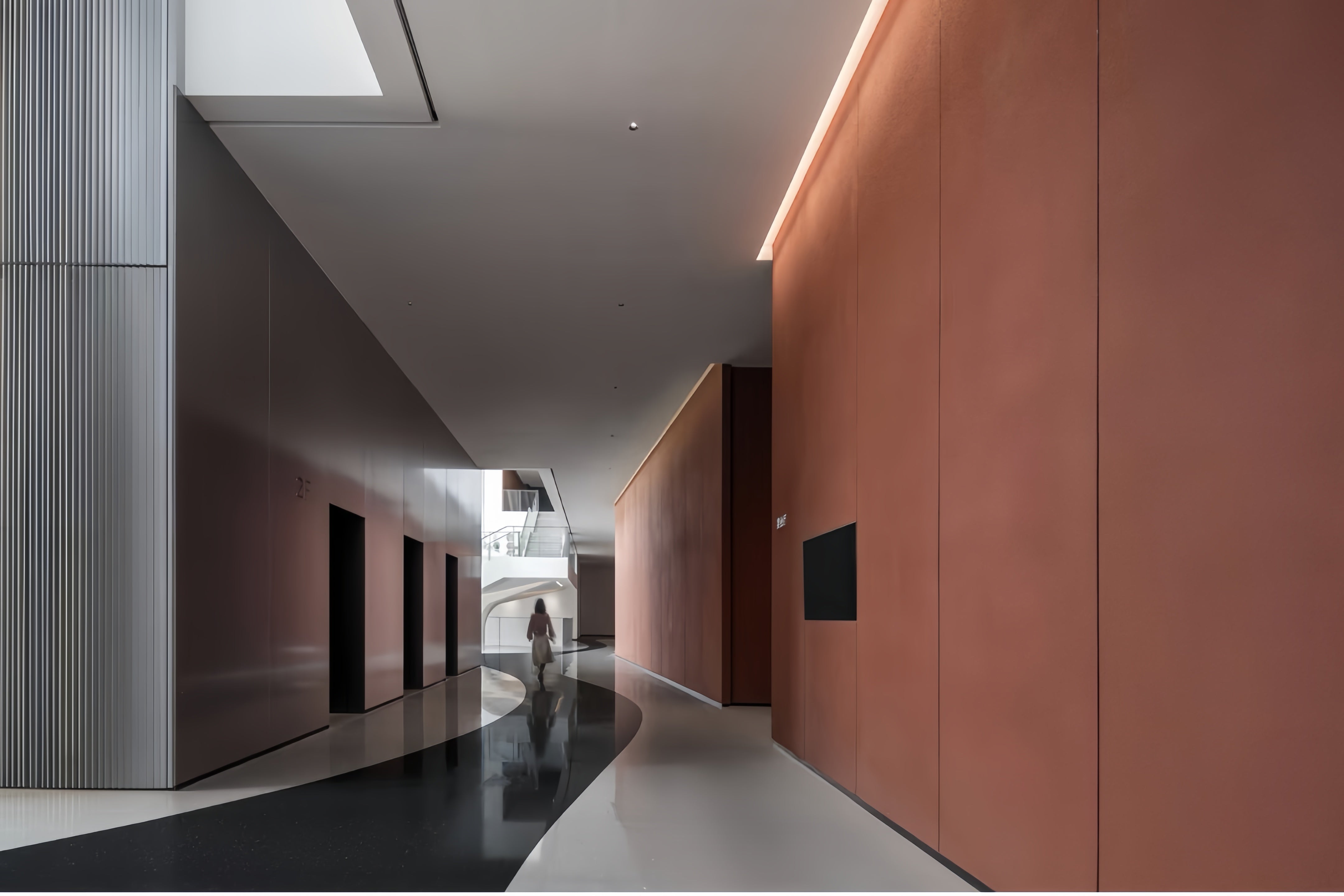
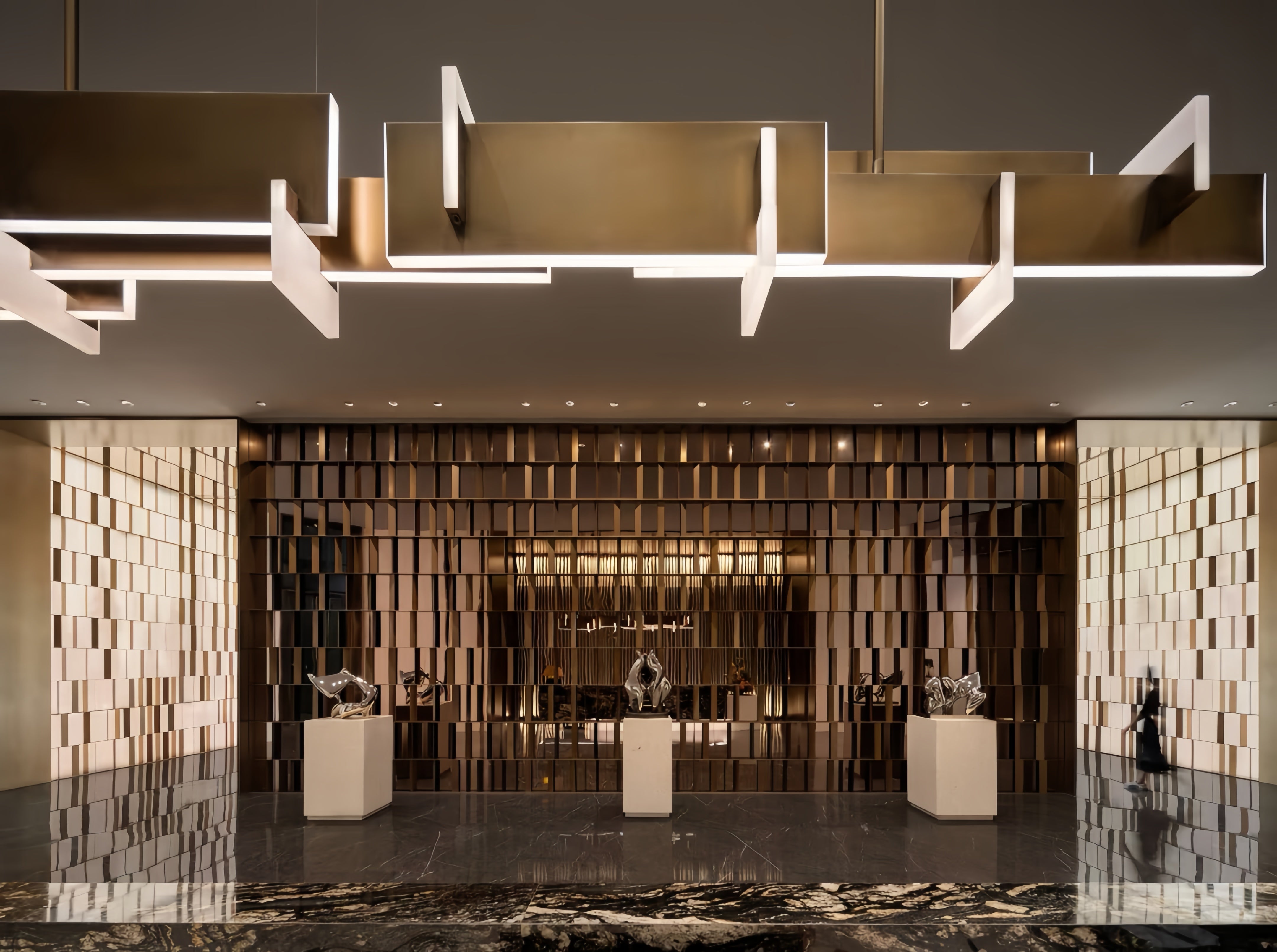
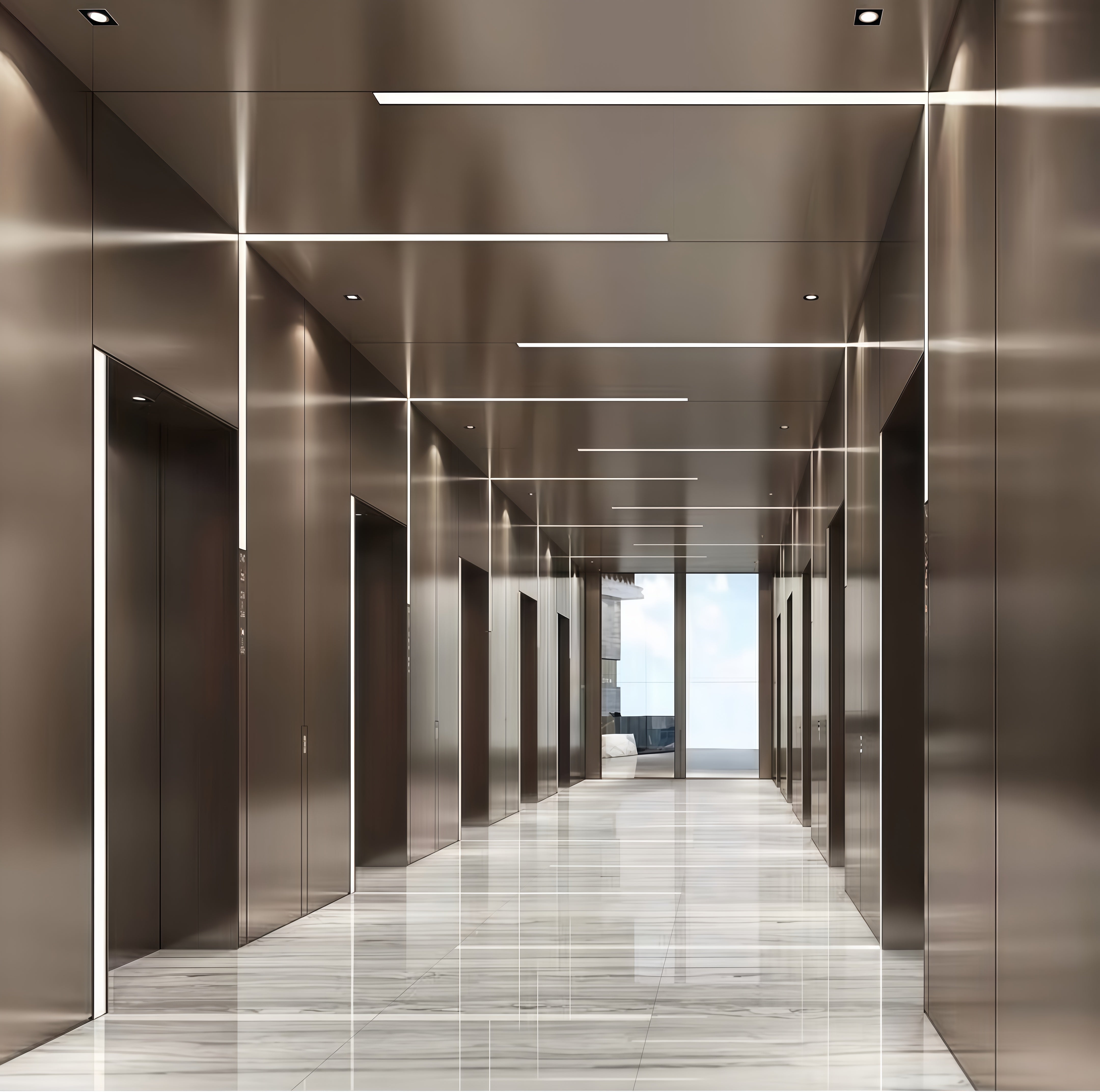
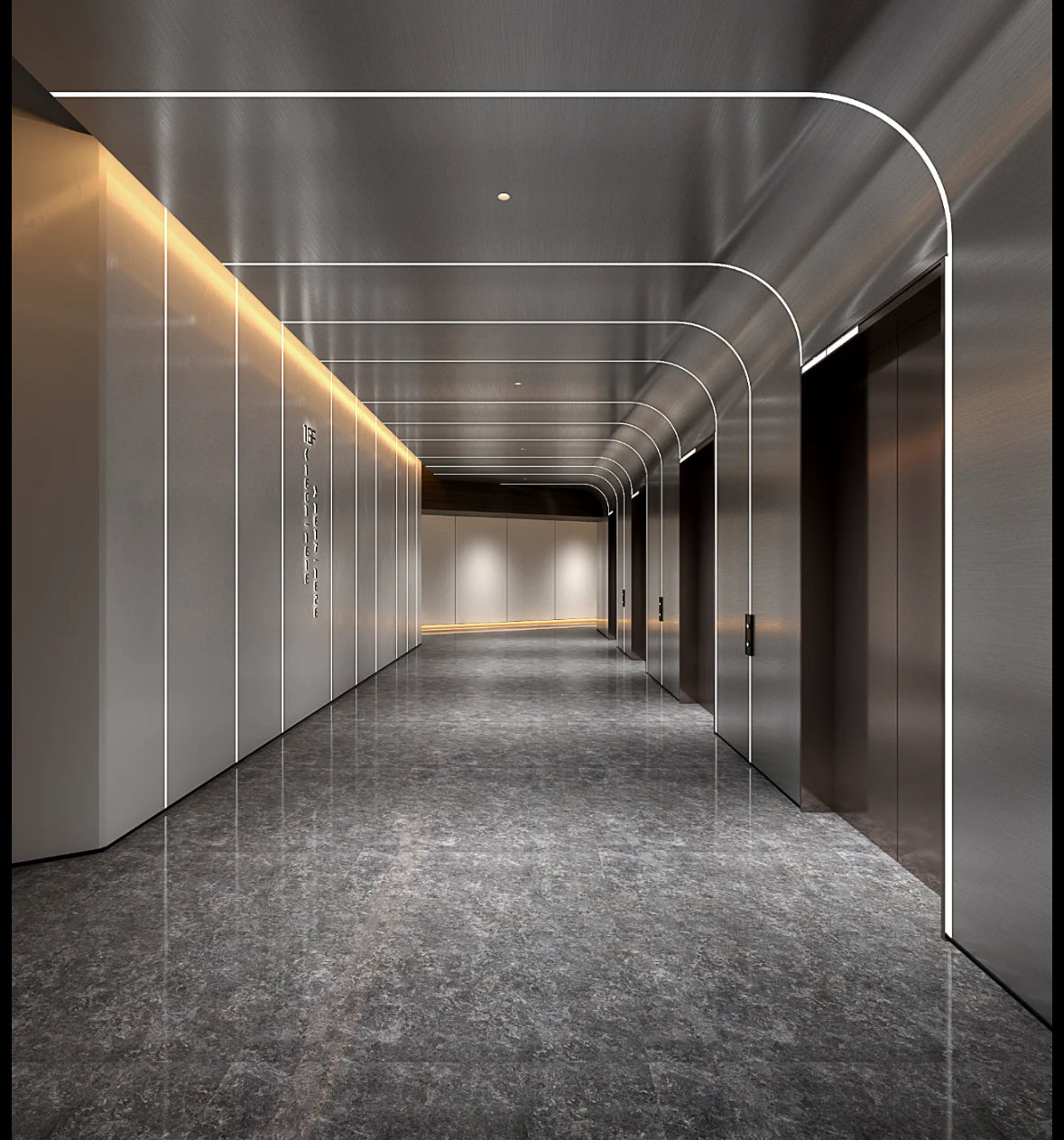
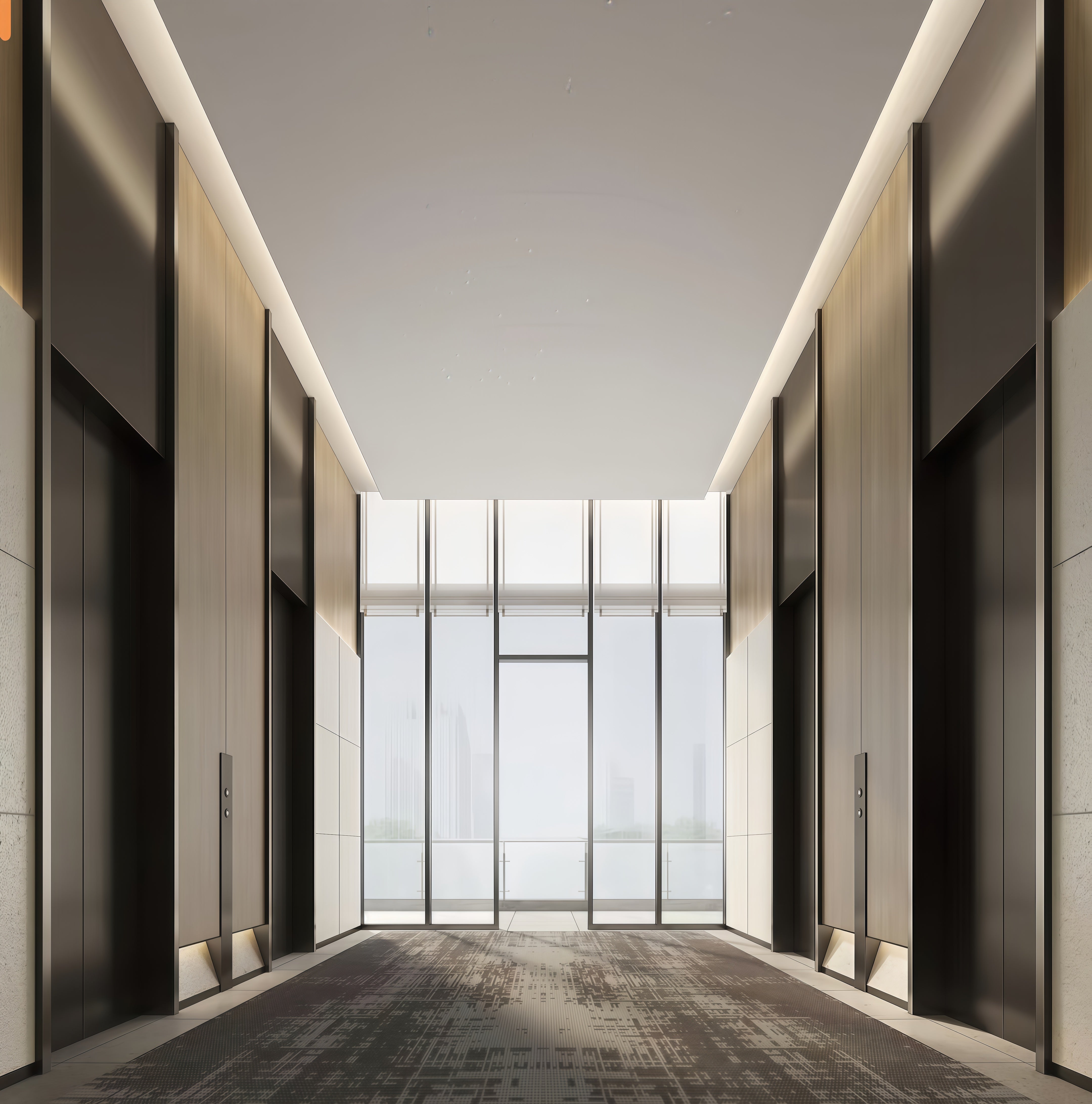
Stainless Steel Interior Wall Panels
Premium stainless steel interior wall panels engineered for the most demanding commercial, institutional, and industrial applications requiring maximum durability, hygiene, and aesthetic appeal. These high-performance panels combine superior corrosion resistance, exceptional strength, and easy maintenance to deliver uncompromising interior cladding solutions for critical environments.
Engineered for interior spaces that demand the highest standards of durability, hygiene, and aesthetic excellence.
- Hygienic & Sterile Environments: The primary choice for hospital operating rooms, commercial kitchens, laboratories, and food processing plants where sanitation is non-negotiable.
- High-Traffic Public Areas: Ideal for airport terminals, transit hubs, lobbies, and corridors, providing exceptional resistance to impact and wear in a sophisticated finish.
- Architectural & Decorative Features: Used to create premium feature walls, elevator interiors, column covers, and reception areas, utilizing finishes from brushed satin to polished mirror.
- Specialty & Wet Areas: Perfect for cleanrooms, pharmaceutical facilities, and high-end restrooms due to its superior resistance to chemicals, moisture, and corrosion.
Superior Hygiene & Cleanability
Its non-porous surface is incredibly easy to sanitize, preventing bacterial growth and meeting the strictest hygiene standards for critical environments.
Durability & Longevity
With exceptional hardness and a Class A fire rating, it withstands impacts, chemicals, and moisture, ensuring a virtually maintenance-free lifespan.
Timeless & Premium Aesthetic
Offers a range of sophisticated finishes, from soft satin to brilliant mirror, to create a modern, high-end look that will not degrade or fade over time.
| Grade | Designation | Properties | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 18-8 Stainless | General corrosion resistance, good formability | Standard commercial, food service |
| 304L | Low Carbon 18-8 | Enhanced weldability, reduced carbide precipitation | Welded assemblies, chemical exposure |
| 316 | 18-10-2 Molybdenum | Superior corrosion resistance, chloride resistance | Marine, chemical, pharmaceutical |
| 316L | Low Carbon 316 | Maximum corrosion resistance, weldability | Critical applications, sterile environments |
| 430 | 16% Chromium Ferritic | Magnetic, lower cost, good corrosion resistance | Budget applications, decorative use |
| Grade | Chromium | Nickel | Molybdenum | Carbon | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 18-20% | 8-10.5% | - | 0.08% max | Standard austenitic |
| 304L | 18-20% | 8-12% | - | 0.03% max | Low carbon austenitic |
| 316 | 16-18% | 10-14% | 2-3% | 0.08% max | Molybdenum enhanced |
| 316L | 16-18% | 10-14% | 2-3% | 0.03% max | Premium grade |
| 430 | 16-18% | - | - | 0.12% max | Ferritic structure |
| Category | Finish Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Mill Finishes | 2B Finish | Cold-rolled, annealed, pickled - smooth, reflective surface |
| 2D Finish | Cold-rolled, annealed, pickled - dull, non-reflective surface | |
| BA Finish | Bright annealed - highly reflective, mirror-like appearance | |
| Mechanical Finishes | #3 Finish | 100-120 grit - coarse directional grain, industrial appearance |
| #4 Finish | 150-180 grit - fine directional grain, architectural standard | |
| #6 Finish | 240-320 grit - very fine grain, premium appearance | |
| #7 Finish | 400+ grit - near-mirror finish, high-end applications | |
| #8 Mirror | Polished to mirror finish - maximum reflectivity | |
| Specialty Finishes | Hairline/Satin | Fine linear grain pattern, hides fingerprints |
| Scotch Brite | Non-directional satin finish, excellent for high-touch areas | |
| Bead Blast | Uniform matte texture, reduces glare and fingerprints | |
| Embossed | Textured patterns for slip resistance and aesthetics | |
| Colored PVD | Titanium, gold, bronze, black coating options |
| Property | 304/304L | 316/316L | 430 | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 515-620 MPa | 515-620 MPa | 450-550 MPa | ASTM A240 |
| Yield Strength | 205-310 MPa | 205-310 MPa | 280-350 MPa | ASTM A240 |
| Elongation | 40-50% | 40-50% | 20-25% | ASTM A240 |
| Hardness | 92 HRB max | 95 HRB max | 88 HRB max | ASTM E18 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 200 GPa | 200 GPa | 200 GPa | ASTM E111 |
| Property | 304/304L | 316/316L | 430 | Units | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 8.0 | 8.0 | 7.7 | g/cm³ | ASTM A240 |
| Melting Point | 1400-1450 | 1375-1400 | 1425-1510 | ºC | - |
| Thermal Conductivity | 16.3 | 16.3 | 26.1 | W/m·K | ASTM E1461 |
| Thermal Expansion | 17.3×10⁻⁶ | 16.0×10⁻⁶ | 10.4×10⁻⁶ | /°C | ASTM E228 |
| Electrical Resistivity | 72 | 74 | 60 | μΩ·cm | ASTM B193 |
| Magnetic Properties | Non-magnetic | Non-magnetic | Magnetic | - | ASTM A342 |
| Thickness | Weight | Max Panel Size | Typical Span | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8mm | 6.4 kg/m² | 1200×2400mm | 300mm | Light decorative, laminated |
| 1.0mm | 8.0 kg/m² | 1500×3000mm | 400mm | Standard commercial |
| 1.2mm | 9.6 kg/m² | 1500×3000mm | 500mm | Food service, healthcare |
| 1.5mm | 12.0 kg/m² | 2000×4000mm | 600mm | Heavy-duty commercial |
| 2.0mm | 16.0 kg/m² | 2000×4000mm | 800mm | Industrial applications |
| 3.0mm | 24.0 kg/m² | 2000×5000mm | 1200mm | Maximum durability |
| Property | Performance | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Rating | Class A Non-combustible | ASTM E84 |
| Flame Spread | 0 (Excellent) | ASTM E84 |
| Smoke Development | 0 (Excellent) | ASTM E84 |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to +800°C | Service conditions |
| UV Resistance | Excellent | No degradation |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (grade dependent) | ASTM G28/G48 |
| Humidity Resistance | Excellent | No effect |
| Finish | Roughness (Ra) | Reflectivity | Applications | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2B | 0.1-0.5 μm | 50-70% | General commercial | Easy cleaning |
| #4 | 0.4-1.2 μm | 30-50% | Architectural standard | Hides scratches |
| #6 | 0.2-0.6 μm | 60-80% | Premium applications | Shows fingerprints |
| #8 Mirror | 0.05-0.1 μm | 85-95% | High-end decorative | High maintenance |
| Hairline | 0.3-0.8 μm | 40-60% | High-touch areas | Fingerprint resistant |
| System Type | Panel Thickness | Max Span | Installation | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Welded Frame | 1.0-3.0mm | 2000mm | Permanent | None |
| Mechanical Fasteners | 1.2-6.0mm | 1200mm | Standard | Limited |
| Clip Systems | 1.0-2.0mm | 1500mm | Professional | Good |
| Cassette Systems | 0.8-1.5mm | 2000mm | Premium | Excellent |
| Adhesive Mount | 0.8-1.2mm | 800mm | Clean appearance | None |
FAQs
Why Choose Stainless Steel Over Other Materials for Interior Wall Panels?
Stainless steel interior wall panels provide unmatched performance in demanding environments where hygiene, durability, and chemical resistance are critical requirements:
Superior Hygiene and Cleanliness:
- Non-porous surface prevents bacterial growth and contamination
- Easy sterilization compatible with all hospital-grade disinfectants
- No organic materials that can harbor bacteria, mold, or allergens
- Smooth surface eliminates crevices where contaminants can accumulate
- Chemical inertness won't react with cleaning agents or disinfectants
- FDA approved for direct food contact applications
Unmatched Durability:
- 40+ year service life in demanding commercial environments
- Impact resistance withstands equipment contact and daily abuse
- Scratch resistance maintains appearance despite heavy use
- Dent resistance superior to aluminum and other lightweight materials
- Corrosion immunity unaffected by moisture, chemicals, and environmental factors
- Temperature stability performs from -200°C to +800°C
Chemical and Environmental Resistance:
- Acid resistance handles most industrial and laboratory chemicals
- Alkali resistance withstands strong cleaning solutions
- Salt water resistance (316 grades) ideal for coastal environments
- Oxidation resistance maintains appearance without protective coatings
- UV stability no degradation from sunlight or artificial lighting
- Humidity immunity unaffected by moisture and steam
Fire Safety Excellence:
- Class A non-combustible rating with zero flame spread
- No toxic gas emission during fire exposure
- Structural integrity maintained at high temperatures
- No smoke development critical for egress and visibility
- Insurance benefits may reduce premiums due to fire safety
Economic Advantages:
- Lowest lifecycle cost despite higher initial investment
- No maintenance painting or refinishing required
- Individual panel replacement possible without system renovation
- High salvage value stainless steel retains significant scrap value
- Energy efficiency reflective surfaces can reduce lighting costs
- Property value enhancement permanent building improvement
Aesthetic Benefits:
- Timeless appearance never goes out of style
- Professional image enhances facility reputation and brand
- Light reflection brightens interior spaces naturally
- Design flexibility multiple finishes and textures available
- Integration capability works with any architectural style
- Consistent appearance no fading, discoloration, or variation
Application-Specific Advantages:
Healthcare Facilities:
- Infection control critical for patient safety
- Easy decontamination between patients and procedures
- Chemical compatibility with all medical cleaning agents
- Impact resistance from equipment and daily operations
Food Processing:
- USDA/FDA compliance for food contact surfaces
- Easy cleaning meets HACCP requirements
- Temperature resistance withstands cooking and refrigeration extremes
- Grease resistance easy removal of cooking residues
Laboratories:
- Chemical inertness won't contaminate experiments or samples
- Easy decontamination between different research projects
- Static control options available for sensitive applications
- Durability withstands laboratory equipment and procedures
How Do You Select the Right Stainless Steel Grade for Interior Applications?
Selecting the optimal stainless steel grade requires careful evaluation of environmental conditions, performance requirements, and cost considerations:
Grade 304/304L (Standard Austenitic):
Best Applications:
- General commercial offices, retail, hospitality
- Standard food service restaurants, cafeterias, break rooms
- Educational facilities schools, universities, training centers
- Light industrial manufacturing, assembly areas
Performance Characteristics:
- Corrosion resistance: Excellent in normal indoor environments
- Formability: Excellent for complex shapes and fabrication
- Weldability: Good (304L superior for welded assemblies)
- Cost: Most economical austenitic grade
- Magnetic properties: Non-magnetic (austenitic structure)
Environmental Limitations:
- Chloride sensitivity: Not recommended for high-chloride environments
- Acid resistance: Limited resistance to strong acids
- Temperature limits: Carbide precipitation above 425°C (304 only)
Grade 316/316L (Molybdenum Enhanced):
Best Applications:
- Healthcare facilities hospitals, clinics, surgical suites
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing clean rooms, sterile processing
- Chemical laboratories research, quality control, testing
- Marine environments coastal facilities, high-humidity areas
- Food processing where chloride cleaning agents are used
Performance Characteristics:
- Superior corrosion resistance: Molybdenum addition enhances performance
- Chloride resistance: Excellent resistance to salt water and chlorides
- Chemical resistance: Better acid resistance than 304 grades
- Pitting resistance: Superior resistance to localized corrosion
- Cost: 20-40% premium over 304 grades
Specific Advantages:
- Pharmaceutical compliance: Meets stringent pharmaceutical standards
- Medical device compatibility: Biocompatible for medical applications
- Chemical processing: Handles most industrial chemicals safely
- Coastal durability: Excellent performance in salt air environments
Grade 430 (Ferritic):
Best Applications:
- Budget-conscious projects where appearance is primary concern
- Decorative applications trim, accents, architectural features
- Low-corrosion environments interior applications with minimal chemical exposure
- Magnetic applications where magnetic properties are beneficial
Performance Characteristics:
- Cost advantage: 30-50% less expensive than austenitic grades
- Magnetic properties: Ferritic structure is magnetic
- Corrosion resistance: Good in mild environments
- Formability: Limited compared to austenitic grades
- Weldability: More difficult than austenitic grades
Limitations:
- Reduced corrosion resistance: Not suitable for harsh environments
- Limited formability: Complex shapes may be difficult
- Brittle at low temperatures: Not suitable for cold environments
- Welding challenges: Requires special procedures and filler metals
Selection Decision Matrix:
Environmental Assessment:
- Chemical exposure - cleaning agents, process chemicals, acids/bases
- Moisture levels - humidity, steam, direct water contact
- Temperature ranges - normal room temperature vs. extreme conditions
- Chloride presence - salt air, chlorinated cleaning agents, food processing
Performance Requirements:
- Corrosion resistance level needed for application lifespan
- Mechanical properties - strength, impact resistance, formability
- Fabrication requirements - welding, forming, machining needs
- Maintenance expectations - cleaning frequency and methods
Economic Considerations:
- Initial material cost vs. performance requirements
- Lifecycle cost analysis including maintenance and replacement
- Risk assessment - cost of failure vs. premium material investment
- Volume discounts available for large projects
Grade Recommendation Guidelines:
Standard Commercial Applications:
- 304/304L: Offices, retail, hospitality, general commercial
- Cost-effective solution for normal indoor environments
- Excellent appearance and adequate performance
Critical Hygiene Applications:
- 316/316L: Healthcare, food processing, pharmaceuticals
- Maximum corrosion resistance for demanding cleaning protocols
- Regulatory compliance for FDA, USDA, pharmaceutical standards
Budget Applications:
- 430: Decorative trim, low-exposure areas, cost-sensitive projects
- Adequate performance for mild indoor environments
- Significant cost savings where premium performance not required
Specialty Considerations:
- 316L preferred for welded assemblies and critical applications
- 304L recommended where welding is required with 304 grade performance
- Custom alloys available for extreme environments (317L, 904L, etc.)
What Are the Installation Requirements for Stainless Steel Interior Panels?
Professional installation of stainless steel interior panels requires specialized knowledge, proper equipment, and attention to detail to achieve optimal performance and appearance:
Pre-Installation Planning:
Material Handling Requirements:
- Protective film must remain on panels until installation completion
- Proper lifting techniques - stainless steel panels are heavy (8-48 kg/m²)
- Storage requirements - flat storage on padded supports, climate-controlled
- Transportation - specialized racks prevent scratching and damage
- Contamination prevention - avoid contact with carbon steel tools and surfaces
Site Preparation:
- Substrate evaluation - flatness tolerance ±2mm over 3m span
- Structural adequacy - panels require substantial support due to weight
- Environmental control - temperature and humidity stable during installation
- Contamination control - clean environment prevents surface contamination
- Access planning - equipment and material handling considerations
Installation System Selection:
Welded Frame Systems:
- Best for: Permanent installations, maximum strength, industrial applications
- Process: Panels welded into structural frames, frames mounted to walls
- Advantages: Maximum strength, permanent installation, seamless appearance
- Requirements: Certified welders, inert gas welding, post-weld cleaning
- Applications: Food processing, pharmaceutical, chemical facilities
Mechanical Fastener Systems:
- Best for: Solid substrates, accessible installations, maintenance requirements
- Process: Panels attached with stainless steel fasteners through face or edges
- Advantages: Field adjustable, removable, straightforward installation
- Requirements: Stainless steel fasteners only, proper hole preparation
- Applications: Commercial kitchens, healthcare, industrial facilities
Clip and Rail Systems:
- Best for: Professional installations, concealed fastening, panel replacement
- Process: Panels hang on wall-mounted rails via stainless steel clips
- Advantages: Clean appearance, easy panel removal, professional installation
- Requirements: Precision installation, quality stainless steel hardware
- Applications: Hospitals, laboratories, high-end commercial
Cassette Systems:
- Best for: Premium installations, maximum accessibility, large format panels
- Process: Panels mounted in frames, frames attached to wall grid systems
- Advantages: Easy maintenance access, excellent appearance, system integration
- Requirements: Precision manufacturing, professional installation, wall depth
- Applications: Clean rooms, pharmaceutical, premium commercial
Critical Installation Considerations:
Contamination Prevention:
- Stainless steel tools only - carbon steel contact causes corrosion
- Clean work environment - prevent iron particle contamination
- Proper cleaning - remove all fabrication residues before installation
- Passivation treatment - restore corrosion resistance after fabrication
- Quality water - use deionized water for final cleaning
Thermal Expansion Management:
- Expansion coefficients - 16-17×10⁻⁶/°C for austenitic grades
- Expansion joints required every 10-12 meters for large installations
- Floating attachment allows panel movement without stress
- Sealant compatibility - use stainless steel compatible materials
- Temperature differential planning for varying conditions
Welding Requirements (if applicable):
- Qualified welders certified for stainless steel welding
- Proper filler metals - matching or overmatching alloy composition
- Inert gas shielding - argon or argon/helium mixtures
- Heat input control - minimize heat-affected zone and distortion
- Post-weld treatment - cleaning, passivation, inspection
Quality Control Procedures:
Pre-Installation Inspection:
- Panel condition - check for damage, scratches, contamination
- Dimensional verification - confirm panels match specifications
- Surface finish - verify finish quality and consistency
- Hardware inspection - ensure all fasteners and clips are stainless steel
Installation Verification:
- Alignment checks - use laser levels and precision measuring tools
- Fastener torque - proper tightening without over-stressing panels
- Gap consistency - maintain uniform spacing throughout installation
- Cleanliness - remove all installation debris and contamination
Post-Installation Requirements:
- Protective film removal - careful removal without surface damage
- Final cleaning - complete cleaning with appropriate stainless steel cleaners
- Passivation treatment - restore full corrosion resistance
- Quality inspection - verify installation meets specifications
- Documentation - record installation details for warranty compliance
Common Installation Challenges:
Surface Contamination:
- Iron particle pickup from carbon steel tools or work surfaces
- Prevention: Use only stainless steel tools and clean work environment
- Correction: Passivation treatment to remove contamination
Scratching and Damage:
- Cause: Improper handling, wrong tools, contaminated work surfaces
- Prevention: Maintain protective film, use proper tools and techniques
- Correction: Professional polishing or panel replacement
Distortion and Warping:
- Cause: Improper support, thermal stress, welding distortion
- Prevention: Adequate support, thermal expansion accommodation
- Correction: Stress relief, re-fabrication if severe
Installation Best Practices:
- Stainless steel fasteners only - no mixed metals
- Proper tool selection - stainless steel or plastic tools
- Clean installation - maintain sterile work environment
- Professional expertise - use experienced stainless steel installers
- Quality materials - specify proper grades and finishes
- Regular inspection - monitor installation quality throughout process
How Do You Maintain Stainless Steel Interior Wall Panels?
Proper maintenance of stainless steel interior panels ensures optimal performance, appearance, and longevity while preserving their corrosion resistance and hygienic properties:
Daily Maintenance Procedures:
Routine Cleaning:
- Frequency: Daily in high-use areas (healthcare, food service)
- Method: Soft cloth or sponge with mild detergent and warm water
- Technique: Clean in direction of grain (brushed finishes)
- Drying: Immediate drying prevents water spots and mineral deposits
- Inspection: Visual check for damage, stains, or contamination
Spot Cleaning:
- Fingerprints: Mild detergent solution or commercial stainless steel cleaner
- Food residues: Warm soapy water, rinse thoroughly
- Grease/oil: Degreasing agents safe for stainless steel
- Water spots: White vinegar solution or commercial spot remover
- Immediate attention: Clean spills and stains promptly
Weekly Deep Cleaning:
Comprehensive Cleaning Process:
- Pre-rinse with clean water to remove loose debris
- Apply cleaning solution appropriate for soil type and finish
- Scrub gently with soft brush or cloth following grain direction
- Rinse thoroughly with clean water to remove all cleaning residues
- Dry completely with soft, lint-free cloth or air dry
- Polish if desired with appropriate stainless steel polish
Cleaning Agent Selection:
- Mild detergents: General cleaning, daily maintenance
- Stainless steel cleaners: Commercial products designed for stainless steel
- Disinfectants: Hospital-grade for healthcare applications
- Degreasers: Food service and industrial applications
- Acid cleaners: Mineral deposits, heat tint removal (use with caution)
Application-Specific Maintenance:
Healthcare Facilities:
- Disinfection protocols: Follow CDC and facility-specific procedures
- Cleaning frequency: Between patients, daily deep cleaning minimum
- Approved disinfectants: Quaternary ammonium, alcohol-based, bleach solutions
- Contact time: Follow manufacturer recommendations for effectiveness
- Documentation: Maintain cleaning logs for regulatory compliance
Food Service Environments:
- HACCP compliance: Follow Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points
- Sanitization: Use food-safe sanitizers approved for stainless steel
- Grease removal: Regular degreasing prevents buildup and contamination
- Temperature considerations: Clean equipment when cool to prevent damage
- Inspection requirements: Regular health department compliance checks
Laboratory Settings:
- Decontamination: Between experiments or sample changes
- Chemical compatibility: Verify cleaning agents won't interfere with work
- Residue removal: Complete removal of all cleaning agents
- Static control: Use anti-static cleaners where required
- Documentation: Maintain cleaning records for quality control
Specialized Cleaning Procedures:
Stubborn Stain Removal:
- Heat tint: Mild acid cleaners or specialized stainless steel cleaners
- Rust stains: Oxalic acid-based cleaners (test in inconspicuous area first)
- Paint/adhesive: Appropriate solvents safe for stainless steel
- Welding discoloration: Pickling paste or professional restoration
- Deep scratches: Professional polishing or panel replacement
Restoration Procedures:
- Surface scratches: Progressive polishing with finer grits
- Dull finish: Commercial stainless steel polish or professional restoration
- Contamination: Passivation treatment to restore corrosion resistance
- Severe damage: Professional evaluation for repair vs. replacement
Maintenance Schedule Recommendations:
High-Traffic/Critical Areas (Operating rooms, commercial kitchens):
- Daily: Basic cleaning and disinfection
- Weekly: Deep cleaning and inspection
- Monthly: Detailed inspection and maintenance
- Annually: Professional assessment and restoration if needed
Standard Commercial (Offices, retail, hospitality):
- Daily: Spot cleaning as needed
- Weekly: General cleaning and inspection
- Monthly: Deep cleaning and detailed inspection
- Annually: Professional maintenance assessment
Low-Traffic Areas (Private offices, storage areas):
- Weekly: Basic cleaning and inspection
- Monthly: Thorough cleaning
- Quarterly: Detailed inspection and maintenance
- Annually: Professional assessment
Maintenance Best Practices:Do's:
- Use appropriate cleaning agents designed for stainless steel
- Clean in direction of grain for brushed finishes
- Rinse thoroughly to remove all cleaning residues
- Dry immediately to prevent water spots
- Test new cleaners in inconspicuous areas first
- Maintain cleaning logs for regulatory compliance
Don'ts:
- Never use chloride-based cleaners (bleach, muriatic acid)
- Avoid abrasive cleaners or steel wool
- Don't use carbon steel tools on stainless steel surfaces
- Never mix cleaning chemicals - dangerous reactions possible
- Avoid excessive heat during cleaning procedures
- Don't ignore stains - prompt attention prevents permanent damage
Professional Maintenance Services:
- Annual inspections by qualified stainless steel specialists
- Restoration services for damaged or deteriorated panels
- Passivation treatment to restore maximum corrosion resistance
- Training programs for facility maintenance staff
- Compliance documentation for regulatory requirements
How Do Stainless Steel Panels Compare to Other Premium Interior Materials?
Stainless steel interior panels offer unique advantages when compared to other premium interior materials, particularly in demanding applications requiring maximum performance:
vs. Aluminum Interior Panels:
Performance Comparison:
- Strength: Stainless steel 2-3x stronger (515-620 MPa vs. 145-280 MPa)
- Corrosion resistance: Stainless steel superior in harsh environments
- Chemical resistance: Stainless steel handles acids, alkalis, and solvents better
- Impact resistance: Stainless steel superior dent and damage resistance
- Temperature range: Stainless steel stable to 800°C vs. 150°C for aluminum
- Weight: Aluminum 65% lighter (2.7 vs. 8.0 g/cm³)
Cost Analysis:
- Initial cost: Stainless steel 150-300% higher than aluminum
- Installation: Stainless steel requires heavier-duty support systems
- Lifecycle cost: Comparable due to stainless steel's superior durability
- Maintenance: Both materials require minimal maintenance
- Replacement: Stainless steel lasts longer in harsh environments
Application Selection:
- Choose stainless steel: Healthcare, food processing, chemical exposure, maximum durability
- Choose aluminum: Standard commercial, weight-sensitive applications, budget constraints
vs. Ceramic and Porcelain Panels:
Durability Comparison:
- Impact resistance: Stainless steel superior - ceramic/porcelain can shatter
- Thermal shock: Stainless steel handles rapid temperature changes better
- Flexibility: Stainless steel can flex without cracking
- Repair: Stainless steel scratches can be polished out; ceramic chips require replacement
- Installation: Stainless steel more forgiving during installation
Hygiene Properties:
- Surface porosity: Both materials non-porous and hygienic
- Chemical resistance: Stainless steel superior to most acids and alkalis
- Cleaning: Both easy to clean, but stainless steel more chemical-resistant
- Sterilization: Stainless steel handles all sterilization methods
- Grout lines: Stainless steel can be installed with minimal joints
Aesthetic Considerations:
- Design flexibility: Ceramic offers more colors/patterns; stainless steel more finishes
- Appearance consistency: Stainless steel maintains appearance better over time
- Light reflection: Stainless steel provides better light reflection properties
- Modern appeal: Stainless steel more contemporary; ceramic more traditional
vs. High-Pressure Laminate (HPL):
Performance Advantages:
- Fire resistance: Stainless steel Class A non-combustible vs. HPL combustible
- Chemical resistance: Stainless steel superior to most chemicals
- Impact resistance: Stainless steel won't chip or delaminate
- Moisture resistance: Stainless steel unaffected; HPL can delaminate
- Temperature resistance: Stainless steel stable at high temperatures
- UV resistance: Stainless steel won't fade; HPL may discolor
Maintenance Comparison:
- Durability: Stainless steel 40+ years vs. 10-15 years for HPL
- Repair: Stainless steel scratches repairable; HPL damage requires replacement
- Cleaning: Both easy to clean, but stainless steel more chemical-resistant
- Replacement: HPL easier to replace but requires more frequent replacement
Cost Analysis:
- Initial cost: HPL 60-80% less expensive than stainless steel
- Installation: HPL lighter and easier to install
- Lifecycle cost: Stainless steel lower due to longer service life
- Performance: Stainless steel superior in demanding environments
vs. Solid Surface Materials (Corian, etc.):
Strength and Durability:
- Impact resistance: Stainless steel superior impact and abuse resistance
- Scratch resistance: Solid surface shows scratches more easily
- Heat resistance: Stainless steel superior temperature performance
- Chemical resistance: Stainless steel handles stronger chemicals
- Repair: Both materials can be repaired, but different methods required
Hygiene Comparison:
- Surface porosity: Both non-porous when properly maintained
- Joint elimination: Solid surface can be seamlessly joined; stainless steel has visible joints
- Chemical compatibility: Stainless steel compatible with all disinfectants
- FDA compliance: Both materials FDA-approved for food contact
- Bacterial resistance: Both excellent when properly maintained
Installation and Fabrication:
- Weight: Solid surface lighter and easier to handle
- Fabrication: Solid surface more easily fabricated on-site
- Installation complexity: Solid surface requires specialized installation
- Field repair: Solid surface more easily repaired in field
Cost-Benefit Analysis Summary:
Stainless Steel Advantages:
- Maximum durability - 40+ year service life
- Superior chemical resistance - handles harsh cleaning agents
- Fire safety excellence - Class A non-combustible rating
- Impact resistance - withstands abuse and heavy use
- Professional appearance - maintains appearance over time
- Regulatory compliance - meets strictest health and safety standards
When to Choose Stainless Steel:
- Critical hygiene applications (hospitals, food processing)
- Chemical exposure environments (laboratories, industrial)
- High-traffic, high-abuse areas (schools, transportation hubs)
- Fire safety critical (high-rise buildings, public assembly)
- Long-term value focus (permanent installations, lifecycle cost priority)
- Professional image important (corporate headquarters, premium facilities)
Alternative Material Selection:
- Aluminum: Standard commercial applications, weight-sensitive installations
- Ceramic/Porcelain: Decorative applications, traditional aesthetics
- HPL: Budget-conscious projects, temporary installations
- Solid Surface: Seamless appearance priority, moderate-use applications
Lifecycle Value Proposition:
- Initial investment: Stainless steel typically highest upfront cost
- Operating costs: Lowest maintenance and replacement costs
- Performance: Superior in demanding environments
- Longevity: Longest service life of premium materials
- Total cost of ownership: Often lowest when considering full lifecycle
- Property value: Highest contribution to building value and marketability
Selection Decision Framework:
- Assess environmental conditions - chemical exposure, humidity, temperature
- Evaluate performance requirements - hygiene, durability, fire safety
- Consider aesthetic goals - modern vs. traditional, maintenance appearance
- Analyze cost factors - initial budget vs. lifecycle value
- Review regulatory requirements - health codes, fire safety, industry standards
- Plan for future needs - facility changes, maintenance capabilities