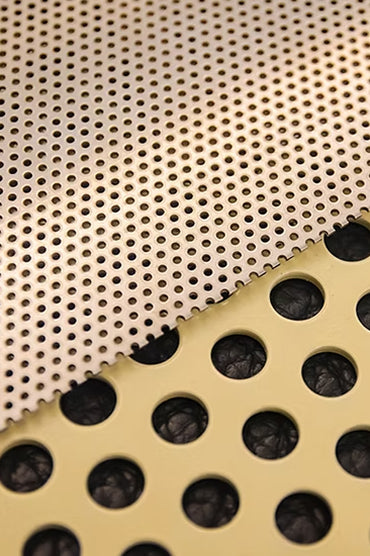


Perforated Metal Sheet for Cladding & Facade
High-performance perforated panels engineered for architectural cladding applications that combine functional ventilation with striking visual aesthetics. These precision-manufactured panels feature customizable perforation patterns that provide controlled airflow, natural lighting, and acoustic performance while maintaining structural integrity and weather protection.
Our perforated panels are engineered to create high-performance building envelopes, transforming facades into dynamic systems that are both functional and visually striking.
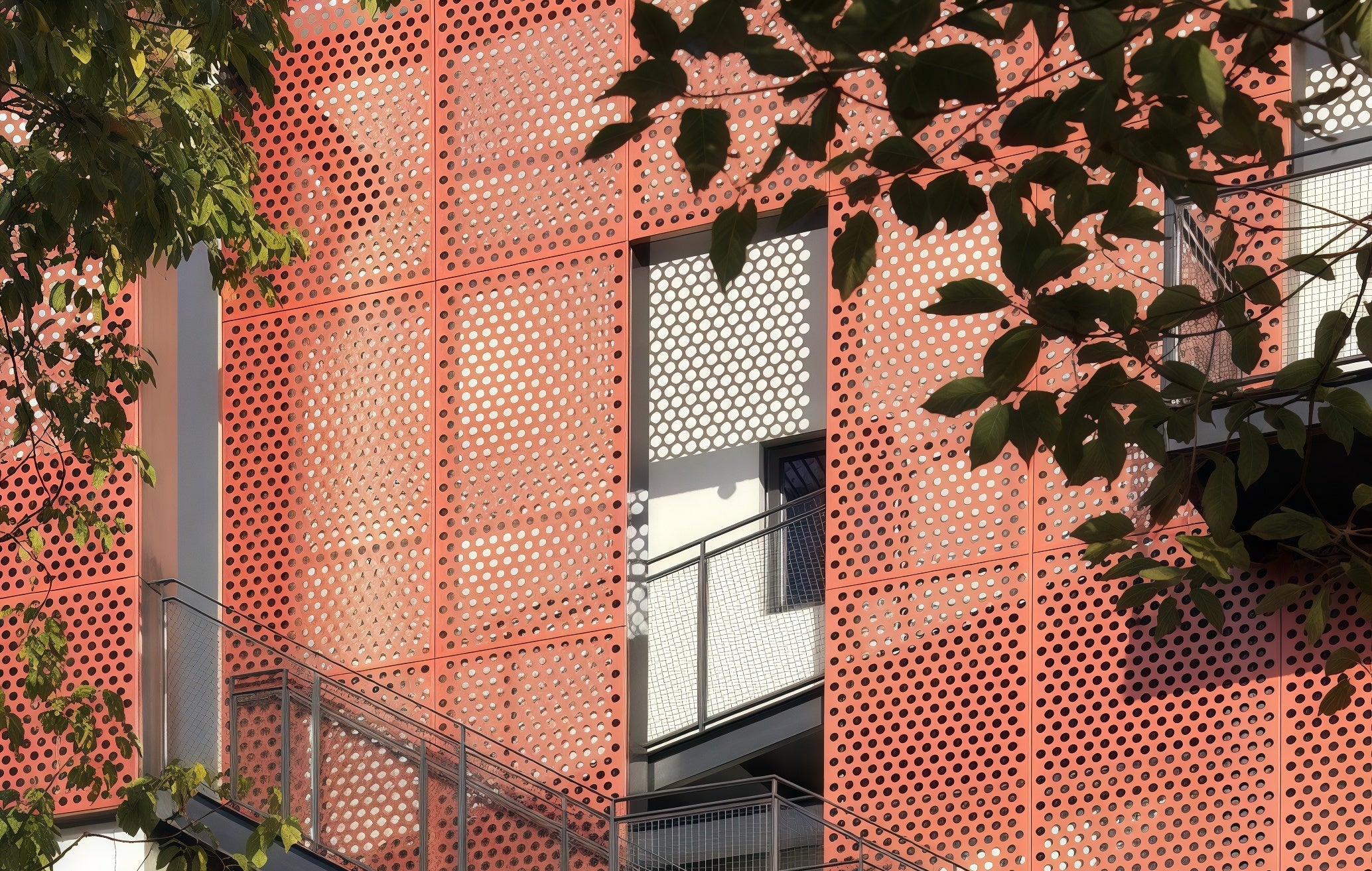
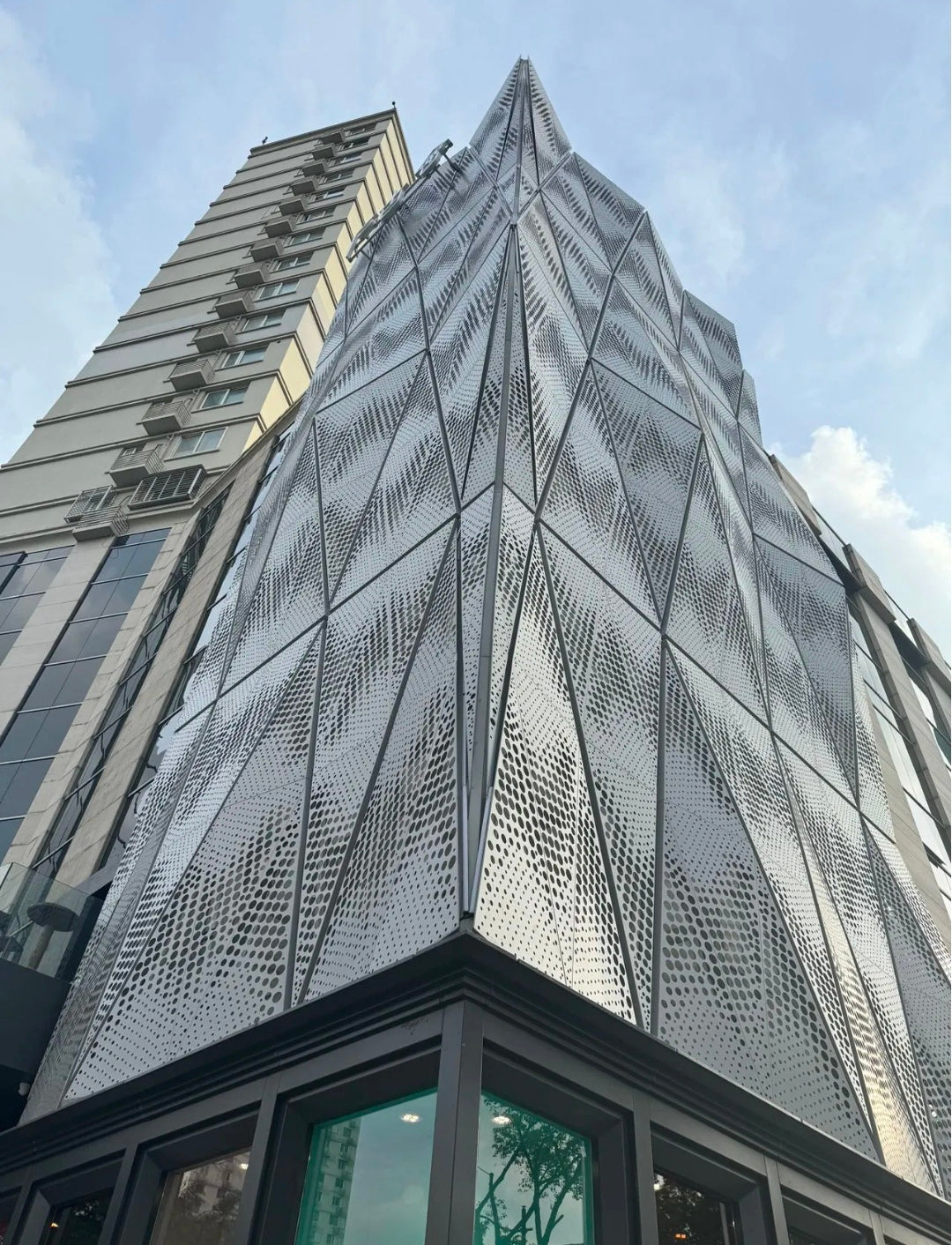
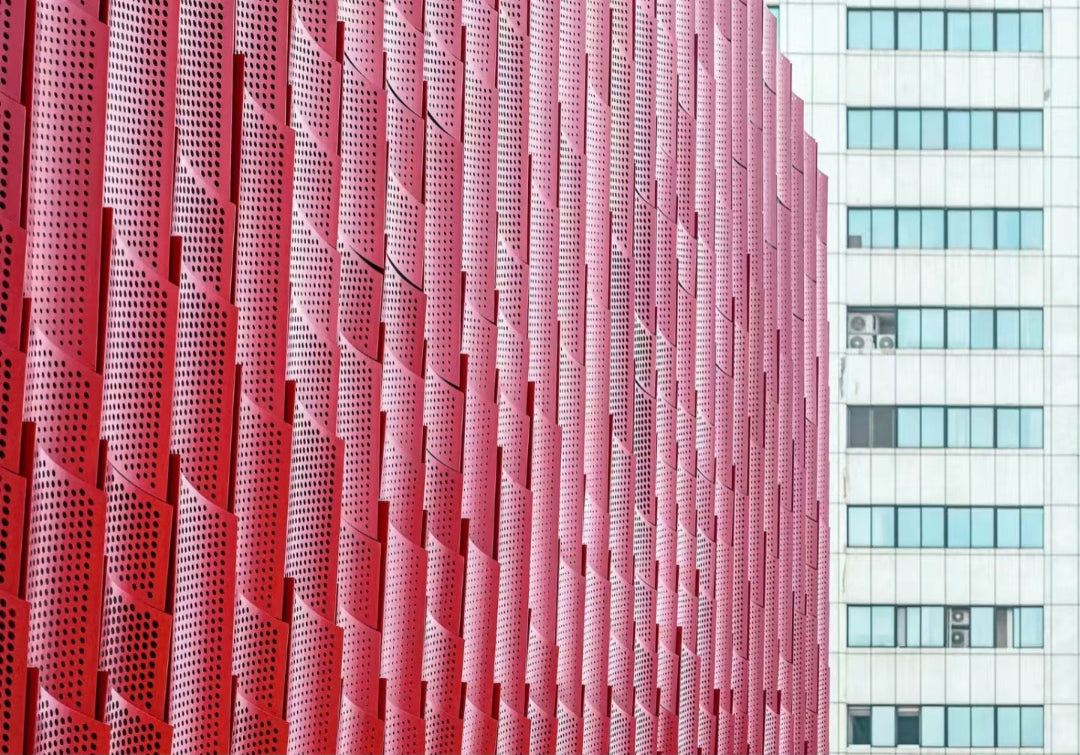
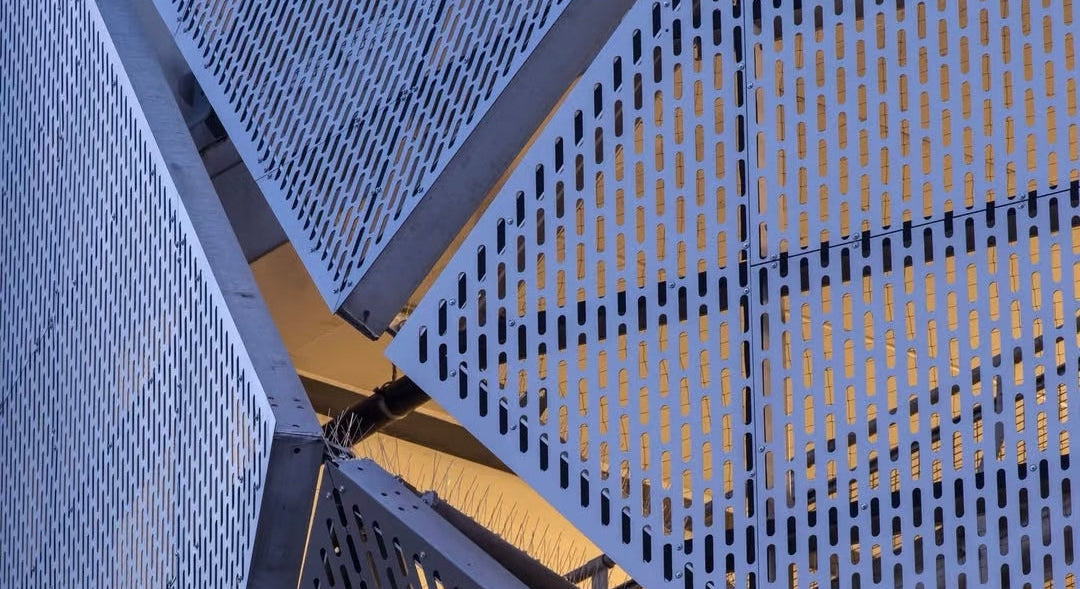
- Architectural Facades & Rainscreens: Used as a primary cladding material to create a building's signature aesthetic, providing texture, depth, and a captivating interplay of light and shadow.
- Parking Structures & Ventilation: The ideal solution for parking garages, offering essential ventilation to disperse exhaust fumes while providing security and enhancing the structure's visual appeal.
- Equipment Screens & Enclosures: Effectively conceals rooftop mechanical units, HVAC systems, and service areas from view while maintaining critical airflow for equipment efficiency.
- Solar Shading & Performance Elements: Strategically employed as a second skin to mitigate solar heat gain, control natural daylight, and act as an acoustic buffer, improving the building's overall energy efficiency and comfort.
Dynamic Architectural Aesthetics
Customizable perforation patterns create a visually stunning facade with texture, depth, and a dynamic play of light and shadow that changes throughout the day.
Functional Environmental Control
The panels provide natural ventilation, solar shading, and acoustic dampening. This reduces HVAC loads, controls daylight, and lowers noise levels, enhancing building performance and occupant comfort.
Weather-Resistant & Durable
Engineered from robust materials like aluminum or steel with advanced PVDF coatings, these panels are designed to withstand wind, rain, and UV exposure, ensuring a long-lasting, low-maintenance building exterior.
| Material Type | Alloy/Grade | Properties | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 3003-H24, 5005-H34 | Lightweight, corrosion resistant, excellent formability | Standard cladding, moderate environments |
| Stainless Steel | 304, 316L | Superior corrosion resistance, high strength | Marine environments, chemical exposure |
| Galvanized Steel | G90, G60 coating | Cost-effective, good corrosion protection | Industrial applications, budget projects |
| Corten Steel | ASTM A588 | Weathering steel, natural rust patina | Architectural features, low-maintenance designs |
| Category | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Round Holes | Ø2mm to Ø50mm diameter |
| Square Holes | 2×2mm to 50×50mm |
| Rectangular Slots | Various width-to-length ratios |
| Hexagonal Patterns | 3mm to 25mm across flats |
| Custom Shapes | Stars, diamonds, decorative patterns |
| Pattern Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Straight Row | Aligned hole patterns |
| Staggered Pattern | Offset rows for maximum strength |
| Custom Layouts | Architectural and artistic designs |
| Gradient Patterns | Variable density across panel |
| Ventilation Level | Open Area Range |
|---|---|
| Low Ventilation | 15-30% open area |
| Standard Ventilation | 30-50% open area |
| High Ventilation | 50-70% open area |
| Maximum Airflow | 70%+ open area (engineering required) |
| Material | Finish Type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | PVDF Fluoropolymer Coating | 25-30μm: 20+ year warranty, premium durability |
| Polyester Powder Coating | 60-80μm: Cost-effective, 10-15 year performance | |
| Anodized Finish | 15-25μm: Natural aluminum appearance, excellent corrosion resistance | |
| Mill Finish | Natural aluminum oxide, basic protection | |
| Steel | Hot-Dip Galvanizing | Maximum corrosion protection (Z275, Z350) |
| Powder Coating | 60-100μm: Color options, good durability | |
| Paint Systems | Primer + topcoat: Custom colors, moderate protection | |
| Weathering Finish | Corten: Natural patina development |
| Property | Aluminum 3mm | Steel 3mm | Stainless 2mm | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Weight | 8.1 kg/m² | 23.5 kg/m² | 15.8 kg/m² | - |
| Perforated Weight* | 5.7-7.3 kg/m² | 16.5-21.2 kg/m² | 11.1-14.2 kg/m² | *30-50% open area |
| Tensile Strength | 145-185 MPa | 400-550 MPa | 515-620 MPa | ASTM B557/A370 |
| Yield Strength | 125-165 MPa | 250-350 MPa | 205-310 MPa | ASTM B557/A370 |
| Elongation | 8-12% | 20-25% | 40-50% | ASTM B557/A370 |
| Open Area % | Airflow (CFM/ft²) | Light Transmission | Structural Efficiency | Acoustic Absorption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15-25% | 150-400 | Low | 85-90% | Low-Medium |
| 25-40% | 400-800 | Medium | 75-85% | Medium |
| 40-55% | 800-1200 | High | 65-75% | Medium-High |
| 55-70% | 1200-1600 | Very High | 50-65% | High |
| Property | Aluminum | Stainless Steel | Galvanized Steel | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 237 W/m·K | 16.3 W/m·K | 50 W/m·K | ASTM E1461 |
| Thermal Expansion | 23.6×10⁻⁶/°C | 17.3×10⁻⁶/°C | 11.7×10⁻⁶/°C | ASTM E228 |
| Melting Point | 660°C | 1400-1450°C | 1538°C | - |
| Density | 2.70 g/cm³ | 8.0 g/cm³ | 7.85 g/cm³ | ASTM B311/A751 |
| Property | Performance | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Rating | Class A Non-combustible (Metal) | ASTM E84 |
| Weather Resistance | 4000+ hours (Coated) | ASTM G155 |
| Salt Spray Resistance | 1000+ hours (Aluminum/SS) | ASTM B117 |
| UV Stability | Excellent (Coated surfaces) | ASTM G154 |
| Thermal Cycling | -40°C to +80°C | ASTM D4329 |
| Wind Load Capacity | Up to 3.5 kPa* | *Engineering required |
| Open Area % | NRC Rating | Sound Absorption | Frequency Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15-25% | 0.15-0.35 | Low | 250-2000 Hz |
| 25-40% | 0.35-0.65 | Medium | 250-4000 Hz |
| 40-55% | 0.65-0.85 | High | 125-4000 Hz |
| 55%+ | 0.85-0.95 | Very High | 125-8000 Hz |
FAQs
What Are the Benefits of Perforated Panels for Building Cladding?
Perforated panels offer unique advantages that combine functional performance with architectural aesthetics, making them ideal for modern building design:
Functional Benefits:
- Natural ventilation reduces HVAC energy costs by 15-30%
- Acoustic performance provides noise reduction (NRC 0.35-0.95)
- Light control creates dynamic facades with controlled daylighting
- Equipment screening conceals mechanical systems while maintaining airflow
- Weather protection with drainage through perforation patterns
Aesthetic Advantages:
- Dynamic visual effects through light and shadow play
- Customizable patterns create unique architectural signatures
- Depth and texture add visual interest to flat facades
- Day/night appearance changes with lighting conditions
- Integration with lighting for dramatic nighttime effects
Performance Features:
- Structural efficiency maintains strength despite perforations
- Lightweight construction reduces building loads
- Corrosion resistance suitable for all climate conditions
- Low maintenance self-cleaning and self-draining design
Applications:
- Parking garage ventilation and screening
- Mechanical equipment concealment
- Facade ventilation systems
- Acoustic barriers and sound control
- Solar shading and light management
Energy Efficiency:
Perforated cladding can significantly reduce building energy consumption through natural ventilation and solar heat gain control.
How Do You Choose the Right Perforation Pattern for Cladding Applications?
Selecting the optimal perforation pattern depends on functional requirements, aesthetic goals, and performance criteria. Here's a comprehensive guide:
Ventilation Requirements:
- Low airflow (15-30% open area): Facade ventilation, weather protection
- Medium airflow (30-50% open area): Standard parking garages, equipment rooms
- High airflow (50-70% open area): Industrial ventilation, mechanical screening
Hole Size Selection:
- Small holes (Ø2-8mm): Maximum structural strength, fine aesthetic appearance
- Medium holes (Ø8-20mm): Balanced performance, standard applications
- Large holes (Ø20mm+): Maximum airflow, bold visual impact
Pattern Types:
- Round holes: Most common, excellent strength-to-weight ratio
- Square/rectangular: Modern appearance, directional airflow
- Hexagonal: Optimal material usage, honeycomb aesthetic
- Custom shapes: Unique design elements, branding opportunities
Acoustic Considerations:
- High-frequency absorption: Small holes (Ø3-8mm), 30-50% open area
- Broadband absorption: Medium holes (Ø8-15mm), 40-60% open area
- Low-frequency control: Large holes (Ø15mm+), 50%+ open area
Structural Requirements:
- High wind loads: Smaller holes, lower open area percentage
- Large spans: Staggered patterns for maximum strength
- Seismic zones: Consider dynamic loading effects
Visual Design Goals:
- Subtle texture: Small, uniform patterns
- Bold statement: Large holes, geometric patterns
- Gradient effects: Variable hole sizes across panel
- Corporate identity: Custom logo or brand patterns
What Materials Are Best for Perforated Cladding Panels?
Material selection for perforated cladding depends on environmental conditions, performance requirements, and budget considerations:
Aluminum (Most Popular Choice):
- Advantages: Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance, easy fabrication
- Best for: Standard commercial buildings, moderate climates
- Finishes: PVDF, polyester, anodized options
- Lifespan: 25-40 years with proper coating
- Cost: Moderate to high, excellent value
Stainless Steel (Premium Option):
- Advantages: Superior corrosion resistance, high strength, minimal maintenance
- Best for: Marine environments, chemical exposure, high-end projects
- Grades: 304 (standard), 316L (marine/chemical)
- Lifespan: 40-50+ years
- Cost: Higher initial cost, lowest lifecycle cost
Galvanized Steel (Budget-Friendly):
- Advantages: Cost-effective, good strength, readily available
- Best for: Industrial applications, temporary structures
- Protection: Hot-dip galvanizing + powder coating
- Lifespan: 15-25 years depending on environment
- Cost: Lowest initial cost
Corten Weathering Steel (Architectural):
- Advantages: Unique rust patina, low maintenance, architectural appeal
- Best for: Feature walls, artistic applications, industrial aesthetics
- Appearance: Natural rust development over 6-18 months
- Lifespan: 50+ years with proper design
- Cost: Moderate, no coating required
Selection Criteria:
- Coastal/marine: Stainless steel or aluminum
- Industrial/chemical: Stainless steel 316L
- Standard commercial: Aluminum with PVDF coating
- Budget projects: Galvanized steel with coating
- Architectural features: Corten or stainless steel
How Much Do Perforated Cladding Panels Cost Per Square Meter?
Perforated panel cladding costs vary significantly based on material, perforation complexity, and project specifications:
Cost Factors:
- Base material type (aluminum, stainless steel, galvanized steel)
- Panel thickness and size requirements
- Perforation pattern complexity (standard vs. custom designs)
- Open area percentage (higher percentages = more processing)
- Surface finish quality (mill finish vs. premium coatings)
- Project quantity and manufacturing volume
Perforation Cost Impact:
- Standard round holes: Minimal cost increase (5-15%)
- Complex patterns: Moderate increase (15-30%)
- Custom designs: Higher increase (30-50%+)
- Very high open area (60%+): Additional engineering costs
Material Cost Comparison:
- Galvanized steel: Most economical base cost
- Aluminum: Moderate cost, best value for most applications
- Stainless steel: Higher material cost, lowest maintenance
- Corten steel: Moderate cost, no coating required
Additional Project Costs:
- Engineering and design for custom patterns
- Installation complexity varies by mounting system
- Structural support may require modifications
- Transportation (perforated panels can be fragile)
Long-term Value:
- Energy savings through natural ventilation
- Reduced HVAC loads lower operating costs
- Low maintenance requirements
- Excellent durability extends replacement cycles
Cost OptimizationTips:
- Choose standard perforation patterns when possible
- Consider aluminum for best cost-performance balance
- Plan for larger quantities to reduce unit costs
- Evaluate lifecycle costs, not just initial price
How Do Perforated Panels Perform in Different Weather Conditions?
Perforated panels are engineered to excel in all weather conditions while providing superior performance compared to solid cladding materials:
Wind Performance:
- Reduced wind loads due to air permeability (20-40% reduction)
- Pressure equalization prevents panel flutter and stress
- Structural efficiency maintained through proper pattern design
- Engineering required for high-wind zones and large panels
- Staggered patterns provide optimal strength-to-weight ratio
Rain and Moisture:
- Self-draining design prevents water accumulation
- Rapid drying through air circulation
- Reduced ice formation in cold climates
- Proper installation with drainage planes essential
- Corrosion resistance varies by material and coating
Temperature Extremes:
- Thermal expansion control through perforation flexibility
- Reduced thermal stress compared to solid panels
- Hot climate performance: Enhanced ventilation reduces heat buildup
- Cold climate performance: No brittleness issues with metal construction
- Thermal cycling resistance: Excellent with proper material selection
UV and Sun Exposure:
- Reduced solar heat gain through perforation shading
- UV-stable coatings (PVDF) provide 20+ year protection
- Anodized finishes excellent UV resistance
- Natural aluminum develops protective oxide layer
- Dynamic shading effects change throughout the day
Coastal and Marine Environments:
- Salt spray resistance: Excellent with aluminum or stainless steel
- Corrosion protection: Enhanced through air circulation
- Material selection critical: 5005 aluminum or 316L stainless recommended
- Regular maintenance: Periodic washing recommended
Industrial and Chemical Exposure:
- Chemical resistance: Stainless steel performs best
- Air circulation helps dissipate harmful vapors
- Protective coatings provide additional chemical barrier
- Material compatibility must be verified for specific chemicals
Performance Advantages:
- Pressure equalization reduces structural stress
- Natural ventilation improves building performance
- Self-cleaning through wind and rain action
- Reduced maintenance compared to solid panels
Installation Considerations:
- Proper drainage design behind panels
- Adequate structural support for wind loads
- Quality sealants and weatherproofing
- Professional installation recommended
What is a Perforated Metal Panel?
A perforated metal panel is a precision-punched sheet (typically aluminum) with uniform holes arranged in custom patterns, designed for architectural cladding, industrial filtration, or acoustic control.
Key Features:
– Material: Made from durable aluminum sheets (0.5–6mm thickness) for corrosion resistance and lightweight installation.
– Fabrication: Created via CNC punching or laser cutting, ensuring ±0.2mm accuracy for complex designs (e.g., round, slotted, decorative shapes).
– Functionality: Balances airflow optimization (10–60% open area) with structural integrity, ideal for façade ventilation or machinery guards.
Common Uses:
– Architectural: Sunshades, decorative screens, or ceiling panels.
– Industrial: Equipment shielding, dust filters, or soundproofing barriers.
For project-specific patterns or load-bearing requirements, consult our team to optimize hole size, spacing, and material grade.